Seals: A Comprehensive Guide
- Mythical Animals
- Mar 17, 2025
- 4 min read
Seals are captivating marine mammals that have drawn the attention of researchers and wildlife lovers alike. Their playful behavior and social interactions make them a joy to observe. In this guide, we will explore the fascinating world of seals, examining their physical traits, behaviors, habitats, and their importance in our marine ecosystems.
What Are Seals?
Seals are part of the order Pinnipedia, which consists of three main families: Phocidae (true seals), Otariidae (eared seals), and Odobenidae (walruses). These marine mammals are distinguished by their streamlined bodies, flippers for swimming, and a thick layer of blubber that keeps them warm in cold waters.
True seals, like the harbor seal, do not have external ear flaps, making them appear more streamlined. In contrast, eared seals, such as sea lions, have visible ear flaps and can move more easily on land. Walruses are famously known for their impressive tusks and distinctive whiskers.
Physical Characteristics
Seals vary greatly in size and shape, adapting remarkably to their specific environments. For instance, while the harbor seal averages around 300 pounds, the elephant seal can weigh as much as 8,800 pounds, making it the largest member of the seal family.
Their outer covering is generally a layer of fur, which serves to insulate them. The coloration of seals can also vary widely, ranging from the mottled brown of the grey seal to the striking dark skin of the leopard seal.
Senses and Adaptations
Seals have developed impressive sensory systems that fit their aquatic lifestyles. Their vision is exceptionally adapted for underwater use, allowing them to see well in low light.
One striking adaptation is their whiskers, called vibrissae. These sensitive appendages help seals detect subtle vibrations within the water, aiding them in finding prey.
Distribution and Habitat
Seals are found in diverse marine environments, from the frigid Polar regions to more temperate waters.
For example, the harp seal thrives in Arctic conditions, while the California sea lion enjoys the warm coastal waters of the Pacific.
Breeding and Molting Habitats
Most seals breed on land, with females typically gathering on ice or rocky shores to give birth and nurse their young. During the breeding season, mothers choose safe locations to support their pups in their early vulnerable days.
Another critical seasonal event is molting. Seals often select secluded beaches to shed their old fur, providing them with privacy during this essential process.
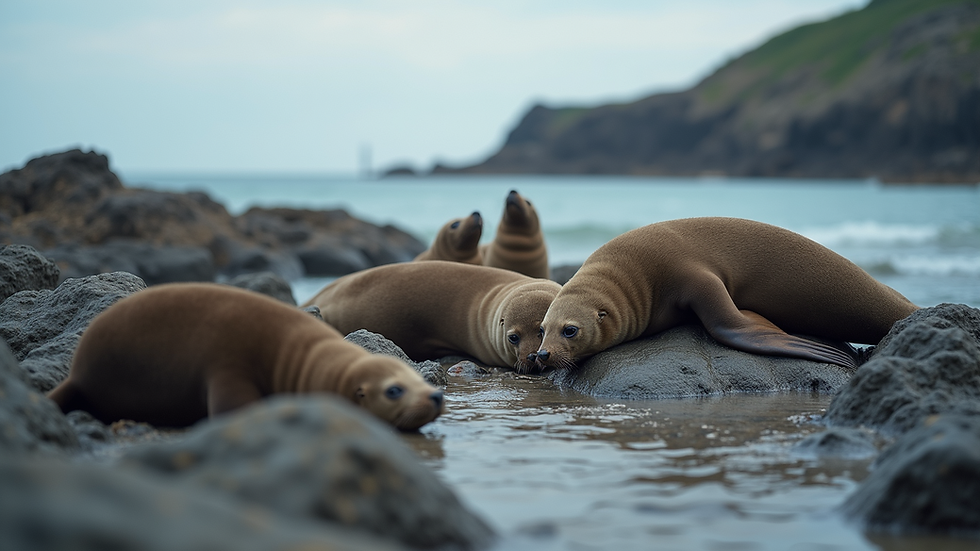

Behavior and Social Structure
Seals display a fascinating range of social behaviors.
Communication
Communication among seals includes various vocalizations and body language.
Newborn pups make high-pitched bleats to signal for their mothers, while adult seals may bark or growl to assert their territory or attract mates.
Foraging
Seals are opportunistic feeders, consuming a broad range of prey, including fish, squid, and crustaceans.
Many species use a hunting technique known as "stunning," where they make rapid strikes to catch their food, relying on their whiskers to sense movements nearby.
Diet and Feeding Habits
Seals primarily eat fish, squid, and crustaceans, depending on their environment.
For example, leopard seals, noted for being apex predators, are notorious for hunting penguins and other seals, showcasing their exceptional hunting skills.
Hunting Techniques
Seals employ various hunting methods. Some hunt cooperatively, corralling schools of fish together, while others dive deep for solitary hunting.
These diverse strategies underline the intelligence and adaptability seals exhibit in their search for food.
Conservation Status and Threats
Many seal species are facing serious threats due to climate change, habitat loss, and human activities.
For instance, the reduction in sea ice is having a significant impact on species like the ice-dependent ringed seal, whose breeding and resting areas are compromised.
Conservation Efforts
To protect seal populations, several measures have been initiated, including habitat conservation, laws against illegal hunting, and the creation of marine protected areas.
Raising public awareness about the role of seals in marine ecosystems is equally important for their future preservation.
Fun Facts About Seals
Breath-Holding Champion: Some seals, such as the Weddell seal, can hold their breath for over 80 minutes and dive to depths of more than 2,000 feet, showcasing their incredible adaptation to deep ocean environments.
Sound Mimicry: Certain seals can mimic sounds they hear around them, further enriching their already diverse vocal repertoire.
Furry Beginnings: Seal pups are born with a thick coat of fur that provides some insulation until their waterproof adult coats begin to develop.
A Closer Look at Seal Conservation
Seals play a vital role in the health of marine ecosystems. Protecting them is not just about preserving a species; it is about maintaining a balance in a larger web of marine life. Whether through supporting marine protected areas or educating others about the risks seals face, we all have a part to play in their conservation efforts.
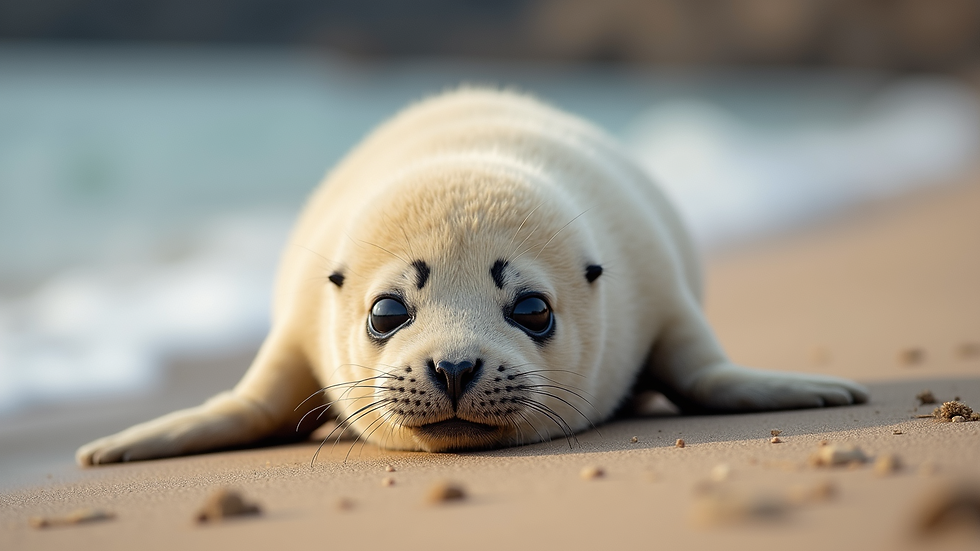

As we enjoy observing these remarkable animals in their natural environments, we must advocate for their conservation. Healthy seal populations are essential for vibrant marine ecosystems, enhancing our connection to the natural world.
Through education, advocacy, and responsible actions, we can work toward a future where seals flourish in our oceans, captivating and inspiring generations to come.


























Comments